Create a Behavior
A behavior is an action that is executed when we change the state of a component or invoke one of its method.
In a behavior you can use all the properties, links, collections, methods or events that your have defined for the current model. You invoke this methods on this object that represents your current component.
Behavior creation
To create a behavior in System Designer:
- click on the Behaviors tab,
- select a system, a model or a component on the right panel,
- click on the '+' button on the left toolbar,
- a dialog is shown,
- select a state,
- then click on Create button,
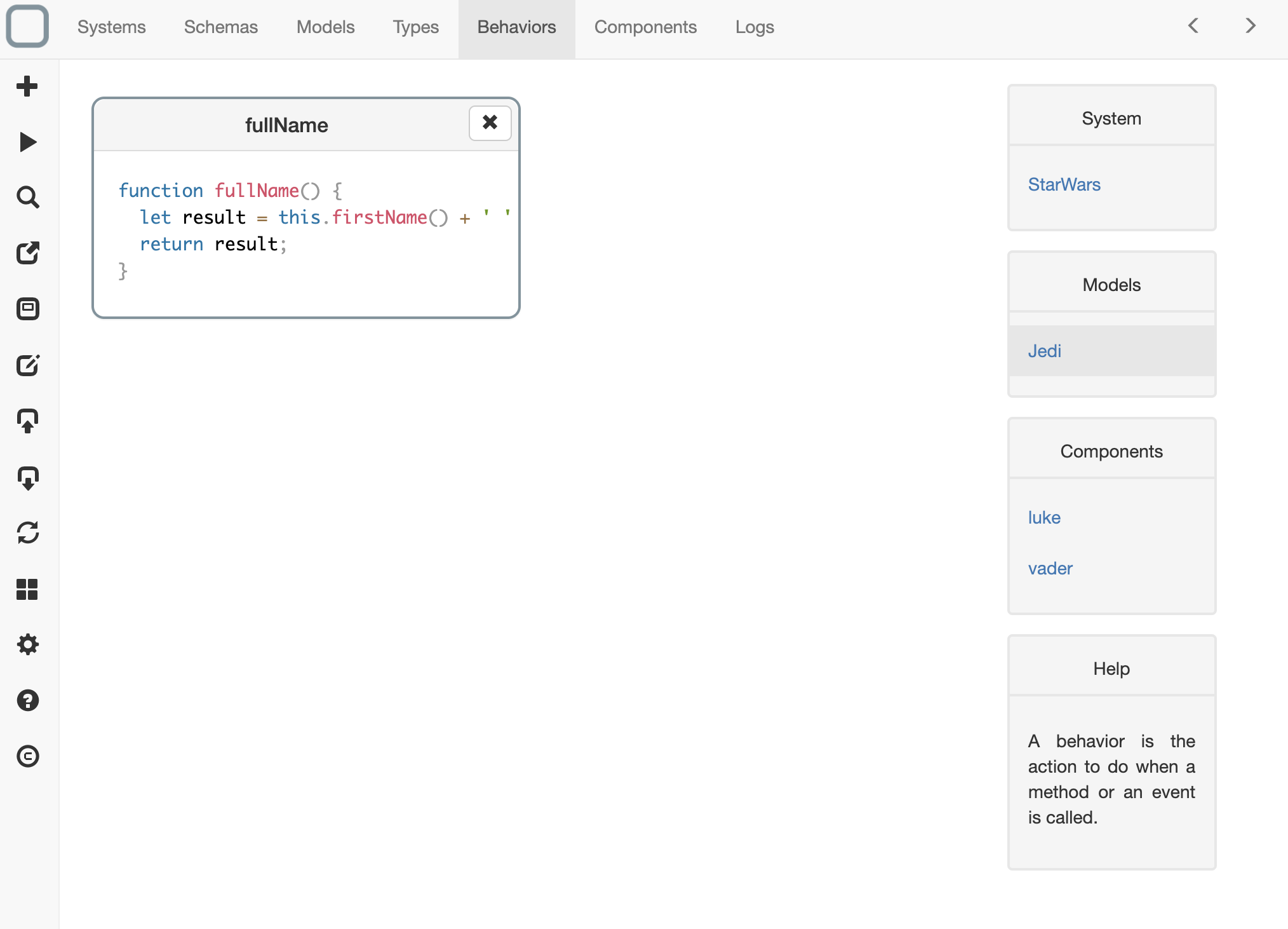
- a new behavior is now created and appears in the Behaviors list:
What is a state?
A state is an event, a method or a change of a property of the model.
Why some behaviors are already there?
When you define a method for a schema, System Designer generates by default their behaviors.
Behavior edition
- click on a behavior,
- an editor will open the content of the behavior,
- you can implement now your behavior:
Use a property
When you define in the schema a property, you have access to it on the component. For example, if you have added in the schema:
{
"_id": "fff15dad-7b8d-4a16-8de8-0c8890f75550",
"_name": "Jedi",
"name": "property"
}
You can directly use it in your code:
// get the value
this.name();
// set a value
this.name('luke');
Model properties are exposed as methods
For every property set in the model, there is a method to get / get its value.
Use a link
When you define in the schema a link, you have access to it on the component. For example, if you have added in the schema:
{
"_id": "fff15dad-7b8d-4a16-8de8-0c8890f75550",
"_name": "Jedi",
"father": "link"
}
You can directly use it in your code:
// get the value of the link
this.father();
// get a component
const vader = this.require('vader');
// set the link value with the component
this.father(vader);
Use a collection
When you define in the schema a collection, you have access to it on the component. For example, if you have added in the schema:
{
"_id": "fff15dad-7b8d-4a16-8de8-0c8890f75550",
"_name": "Jedi",
"children": "collection"
}
You can directly use it in your code:
// get collection value
// get all the collection
// it will be an array of components
this.children();
// get the firt element of the collection,
// a component
this.children(0);
// set collection value
// init the collection
this.children([]);
// get a component
const vader = this.require('vader');
// add the component at the first place of the collection
this.children(0, vader);
// add the component at the last place of the collection
this.children().push(vader);
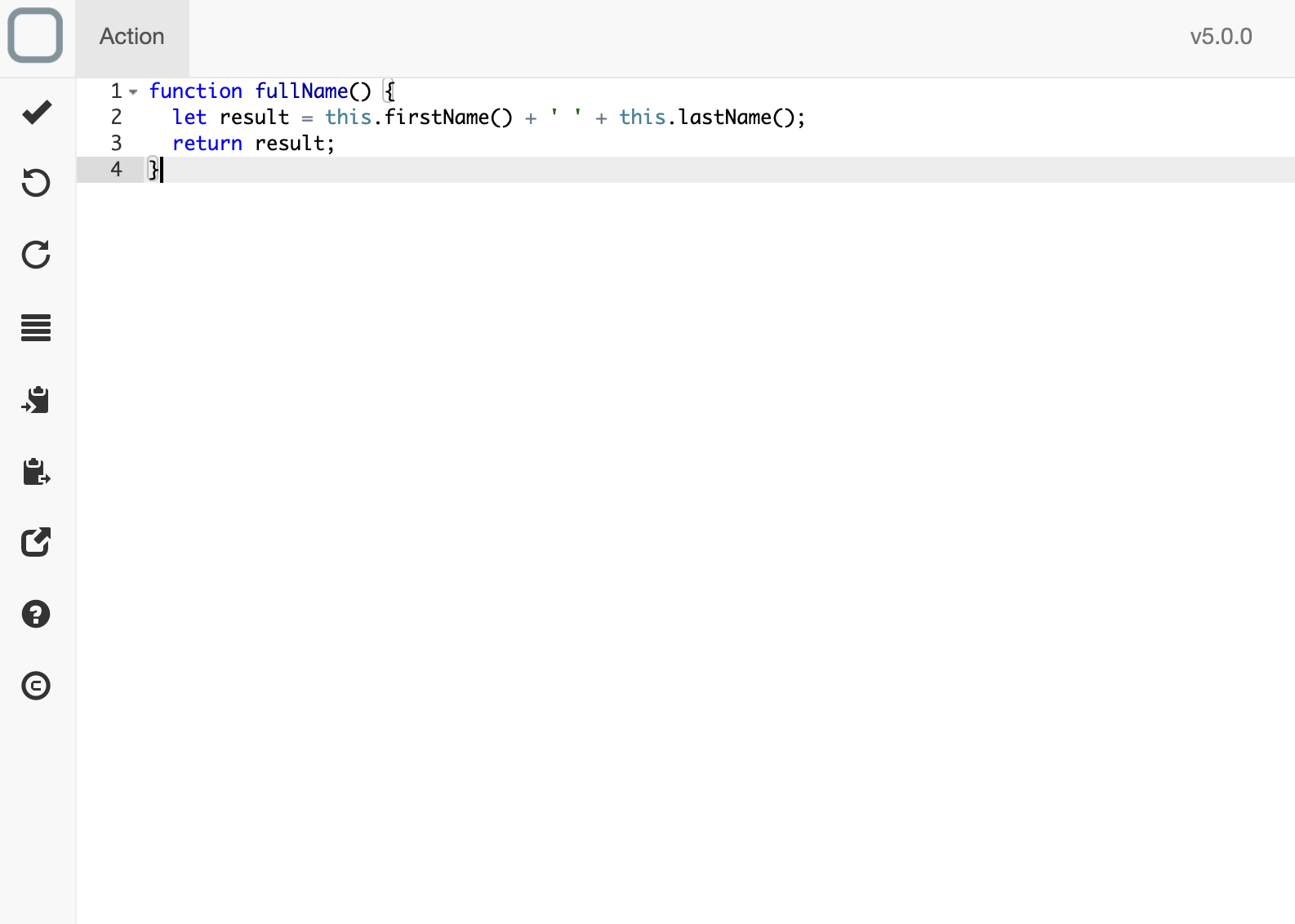
Use a method
When you define in the schema a method, you have access to it on the component. For example, if you have added in the schema:
{
"_id": "fff15dad-7b8d-4a16-8de8-0c8890f75550",
"_name": "Jedi",
"fullName": "method"
}
You can directly use it in your code:
// invoke the method
this.fullName();
Use an event
When you define in the schema a event, you have access to it on the component. For example, if you have added in the schema:
{
"_id": "fff15dad-7b8d-4a16-8de8-0c8890f75550",
"_name": "Jedi",
"changed": "event"
}
You can directly use it in your code:
// trigger an event
this.changed();
Use _Component class APIs
By default, your component inherits from _Component model, so you can use:
- this.id(): to get the id of the component,
- this.destroy(): to destroy a component (you can override this method for your needs) and
- this.require(id : string) : _Component: to require a component.
// require a component
this.require('luke').name();
Call a parent method
In certain cases, you will need to call the parent method in your code. To do it just require the parent class and pass the context as first parameter. Example:
// call fullName method of Person with current context
this.require('Person').fullName(this);
Use logger component APIS
You can require the logger component to log messages. You can use:
- this.require('logger').debug(msg: any): to log a debug message,
- this.require('logger').info(msg: any): to a log an information message,
- this.require('logger').warn(msg: any): to a log a warning and
- this.require('logger').error(msg: any): to a log an error.
You can also specify the level of your logs:
- this.require('logger').level(level: ['off', 'debug', 'info', 'warn', 'error']): set a level for your logs.
// log an information message
this.require('logger').info('this is an message');
Use db component APIS
All the components are stored at runtime in a data store that you can access with System Runtime APIs. You can use them in your behaviors by requiring the db component.
Let's imagine you have created a Person schema and that you want to get the number of person component created:
- require the db component,
- call collections method to get all the collections of models,
- get Person collection and
- call count method on this collection.
// get the number of created components
this.require('db').collections().Person.count();
You can use all these APIs on a collection:
- count(): number: count the number of created components,
- find(query: object): find components with a query,
this.require('db').collections().Person.find({
'firstName': 'Luke'
});
- insert(component: object): create a component,
this.require('db').collections().Person.insert({
'_id': 'luke',
'firstName': 'Luke'
});
- update(query: object, update: object): update a component and
this.require('db').collections().Person.update({
'_id': 'luke'
}, {
'firstName': 'Luke'
});
- remove(query: object): delete a component.
this.require('db').collections().Person.remove({
'_id': 'luke'
});
For more information go to the System Runtime documentation
Advanced mode
First, you need to activate advanced mode. To do so, go to System Designer configuration panel and click on Advanced mode checkbox. Then you a new tab called Behavior will appear when you edit a behavior. Click on this tab to override some internal values for the current behavior.
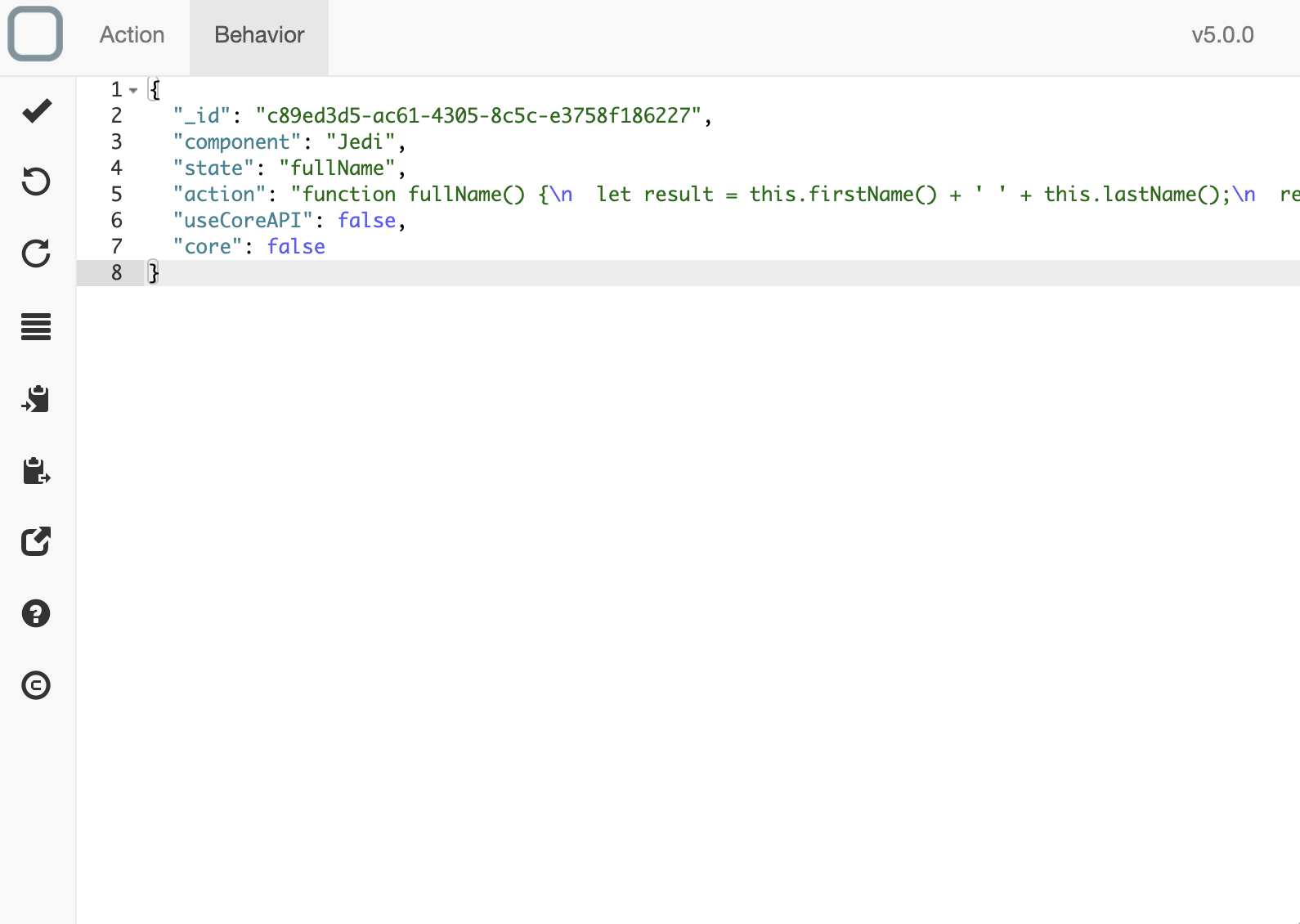
You can for example
- enable the use of internal APIs with useCoreAPI property or
- avoid the exportation of the method with core property.
You will find here the list of internal APIS that you can use.